In the contemporary landscape of wearables, sleep trackers have become a ubiquitous feature in smartwatches and smartbands. These trackers provide users with valuable insights into the duration and patterns of their sleep. However, the underlying mechanism of how they perform this task may pique your curiosity. How do they accurately discern between wakefulness and slumber?
During our visit to Huawei’s headquarters in Shenzhen, China, we had the privilege of conversing with Gong Yuansong, Vice President of Smart Wearables and Health Product Line at Huawei Consumer Business Group. Our discussion revolved around the intricate workings of sleep trackers.
The Trifecta of Sensors
The operation of a sleep tracker hinges on a trio of sensors seamlessly integrated into the smartwatch or smartband. First in the ensemble is the heart rate sensor, which keenly detects a gradual deceleration in heart rate, a telltale sign of the onset of sleep.
The second sensor focuses on physical movements. Leveraging sensors like acceleration and a gyroscope, the device astutely picks up subtle shifts in movement, serving as an indicator of the transition into a sleep state.
The third sensor is the skin temperature sensor. Ordinarily, when sleep beckons, the surface temperature of the body experiences a dip due to reduced physical activity. This temperature decline is diligently captured by the sensor, further confirming the initiation of sleep.
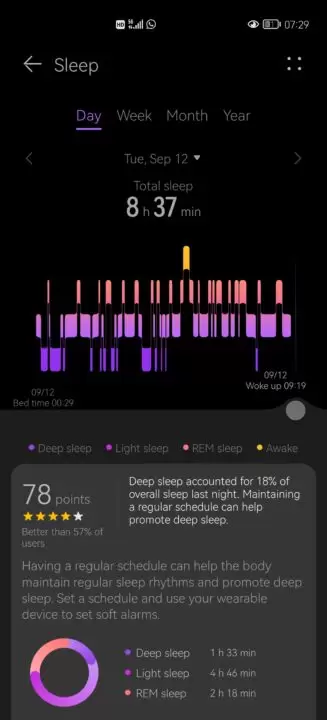
These three datasets are meticulously amalgamated to create a holistic representation of your sleep activity. Smartwatches often empower users with the ability to distinguish between the phases of light and deep sleep.
Results and Health Insights
The results of sleep monitoring are thoughtfully synthesized and presented on the smartwatch’s display, with a more comprehensive breakdown accessible through a dedicated smartphone app. Integrated health apps frequently provide guidance, assuming the role of a “sleeping coach” to aid in enhancing sleep quality. Nevertheless, the counsel they offer tends to be general in nature. For personalized recommendations, it is prudent to seek the counsel of medical professionals.
Nonetheless, the sleep tracking data serves as a valuable point of reference for addressing sleep-related concerns in a timely manner. As an illustration, Huawei’s GT 4 smartwatch introduces a groundbreaking sleep condition detector known as “Sleep Apnea,” a potentially perilous condition marked by interrupted breathing during slumber. Recognizing signs of Sleep Apnea enables users to promptly seek medical guidance and intervention.
Tracking Beyond Conventional Scenarios
Presently, sleep trackers excel primarily in standard sleeping conditions, such as lying in bed. They grapple with challenges when monitoring sleep in unconventional environments, like during bus rides or air travel. The complexity arises from factors that can disrupt sensor accuracy, particularly motion sensors, which find it demanding to decipher sleep patterns amid a moving backdrop.
Notably, Huawei is actively engaged in refining its sleep tracker feature to operate effectively even in unconventional settings. Through collaborations with aerospace entities, Huawei is exploring methods to ensure that the sleep tracker functions reliably when users are in the midst of slumber during a flight.
In essence, Huawei’s unwavering commitment to advancing health tracking features underscores its dedication to enriching the daily lives of users through innovative technology.

